背景
近几天,我成功解包了游戏《ご注文はうさぎですか?? Wonderful Party!》(PSV),在KUN的建议下,我决定记录下这次解包的经历,(顺带本文参考了在遇到自己完全不会的技术栈时应该如何做?的结构编写)
必要性
实际上,我们解包大多数依赖于别人写的工具(当然如果没有的话有可能你得自己写一个,这很麻烦...),但是大部分情况通过网络上的工具就可以搞定,所以如何快速寻找这些工具就显得很重要了
方法论
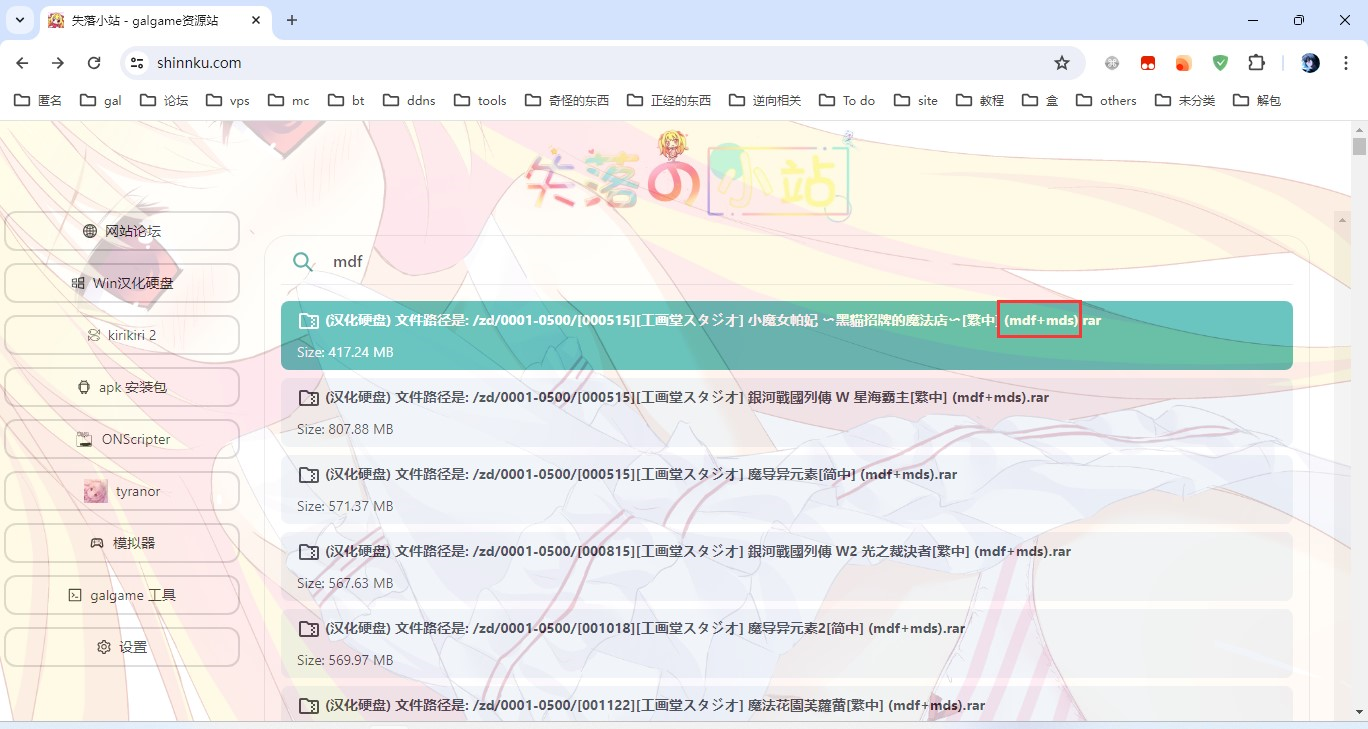
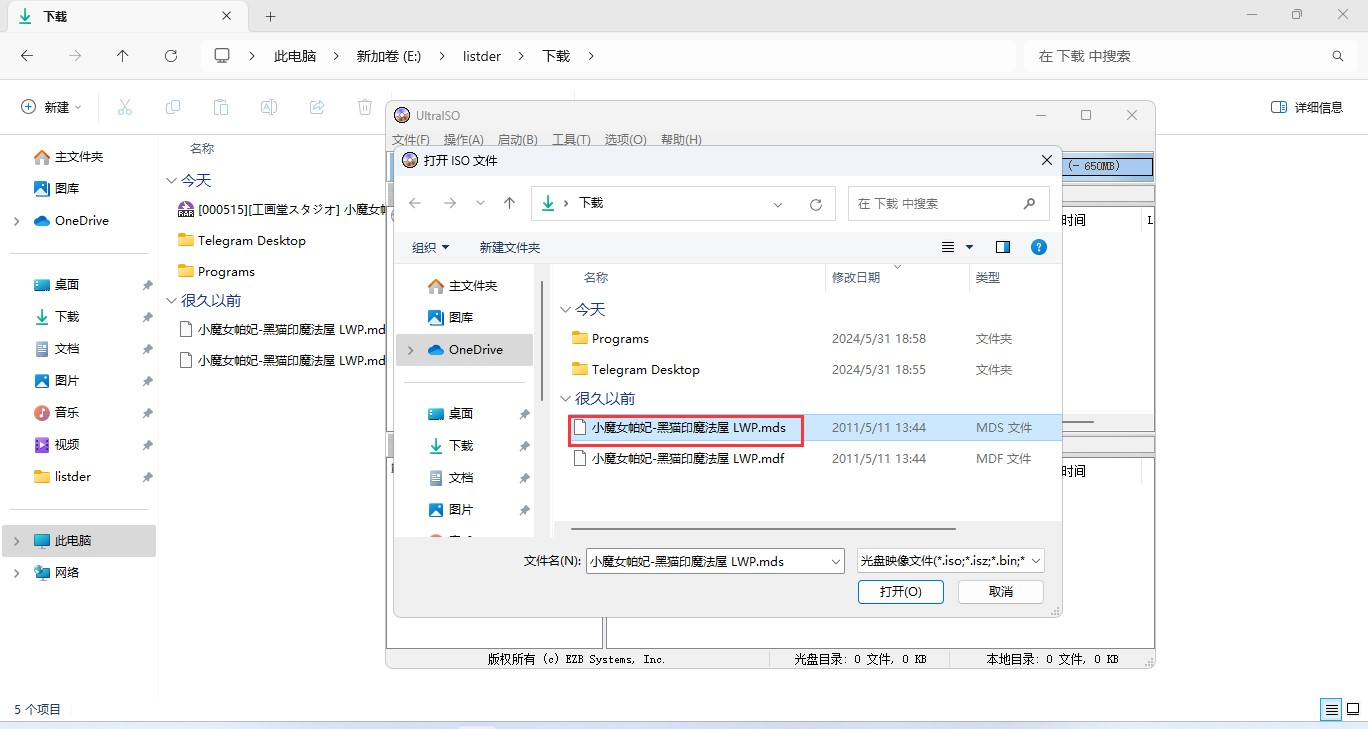
以《ご注文はうさぎですか?? Wonderful Party!》(PSV)为例,首先我们发现,这是一个单文件,文件名为PCSG00786_FULLGAME_01.00_C9_V2.0.vpk,这是一个未知扩展名的文件,所以我们首先应当用16进制编辑器查看
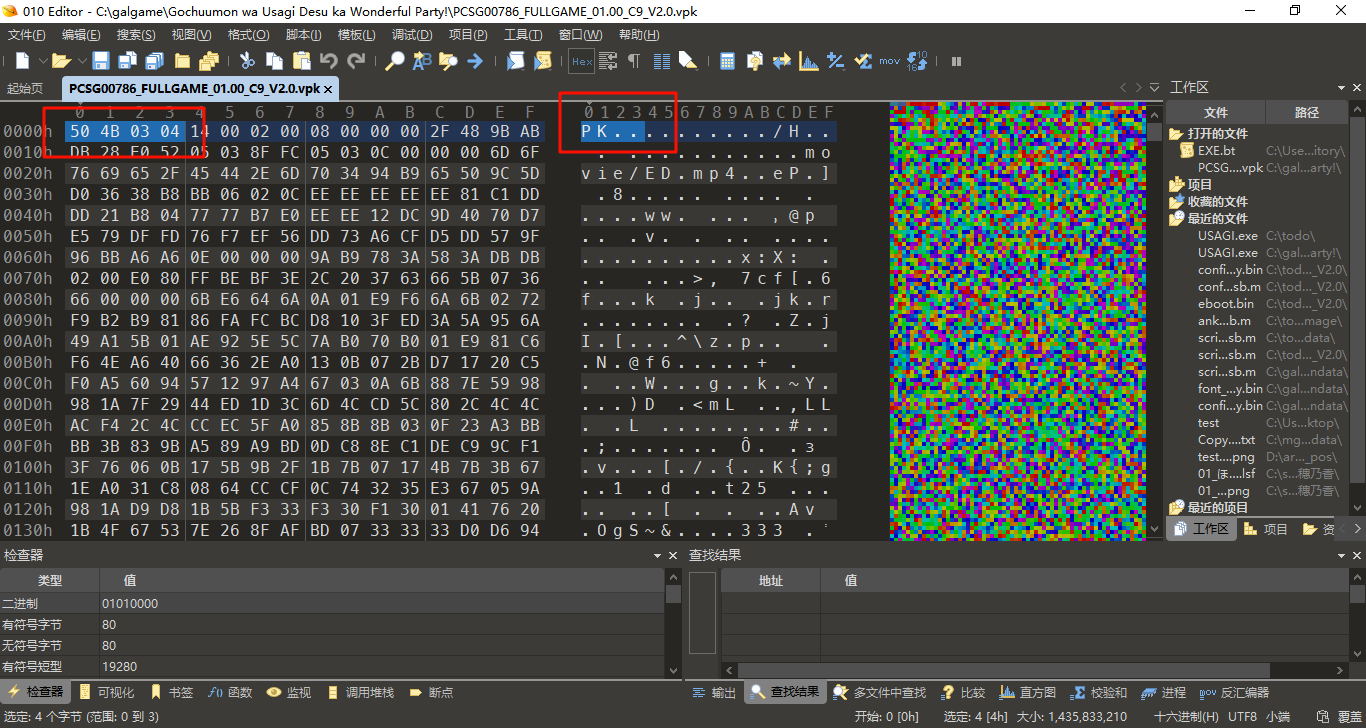
对于这种情况我们应该先确认文件头(此处为50 4B 03 04),然后用Google查找这个文件头,看看这个格式是什么格式 (其实有个更取巧的办法,就是访问List of file signatures,然后直接Ctrl-F来进行查找)
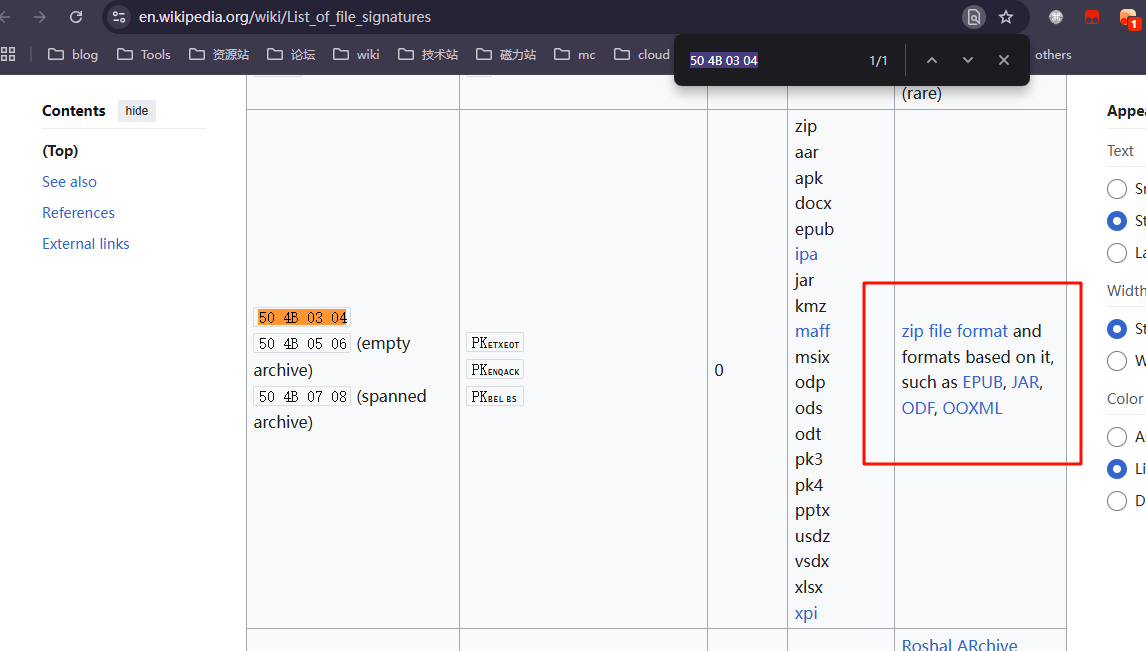
zip file format and formats based on it, such as EPUB, JAR, ODF, OOXML
显然,我们的文件很有可能是用zip直接压缩而来,尝试使用7-zip打开
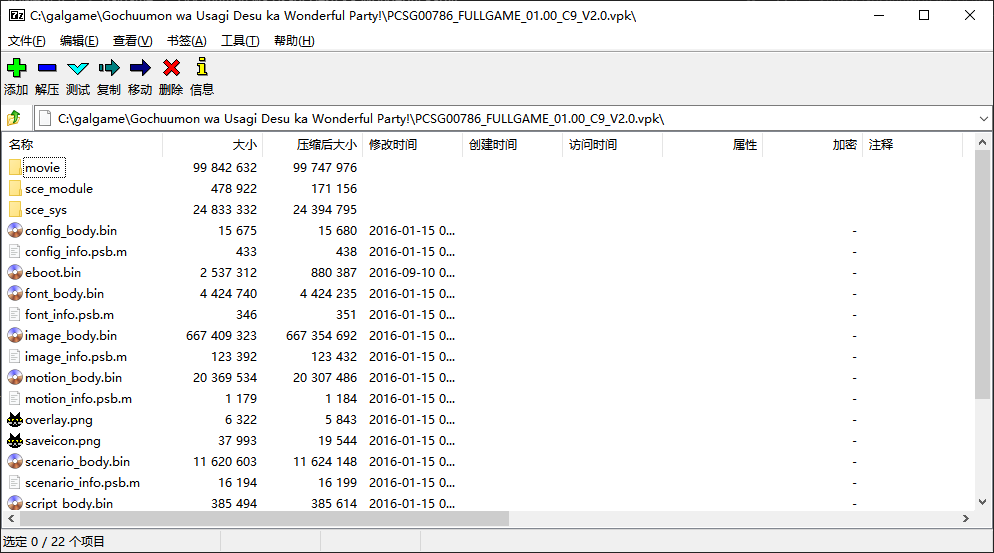
成功了,现在我们就完成了第一步
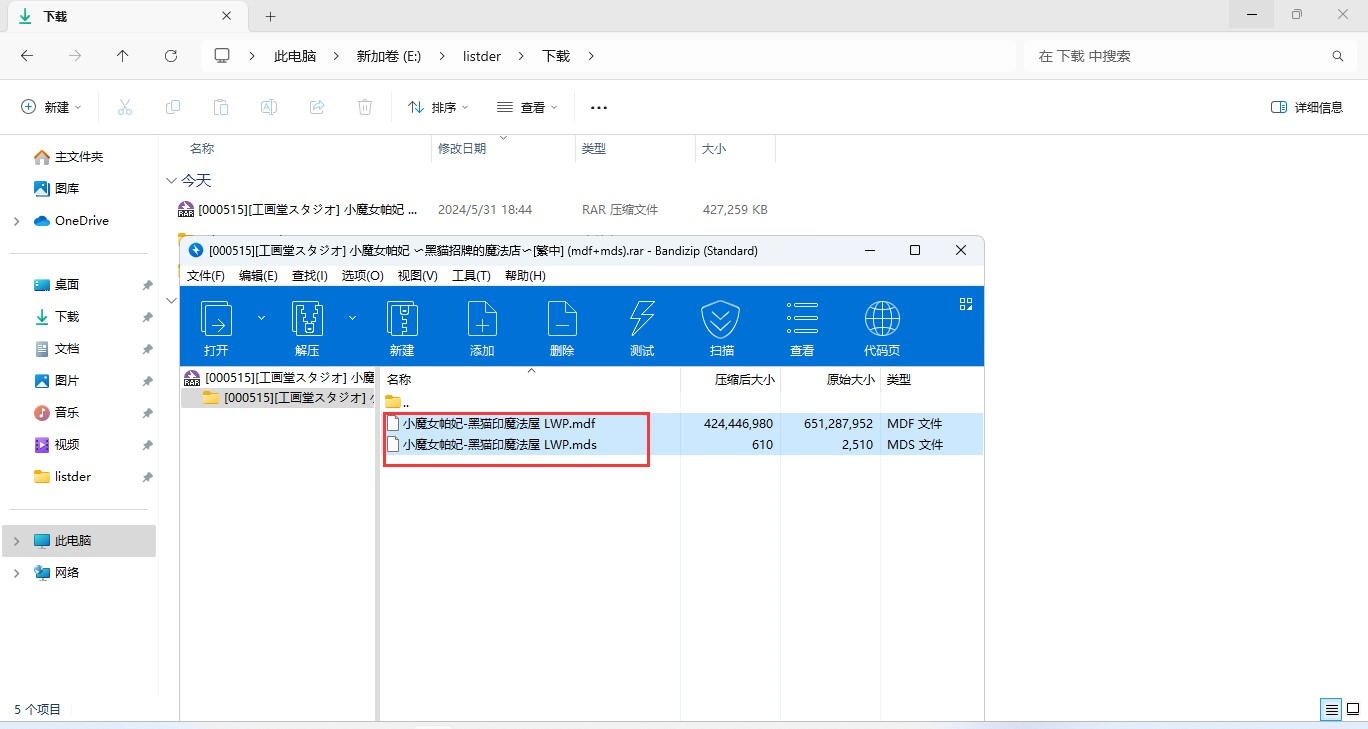
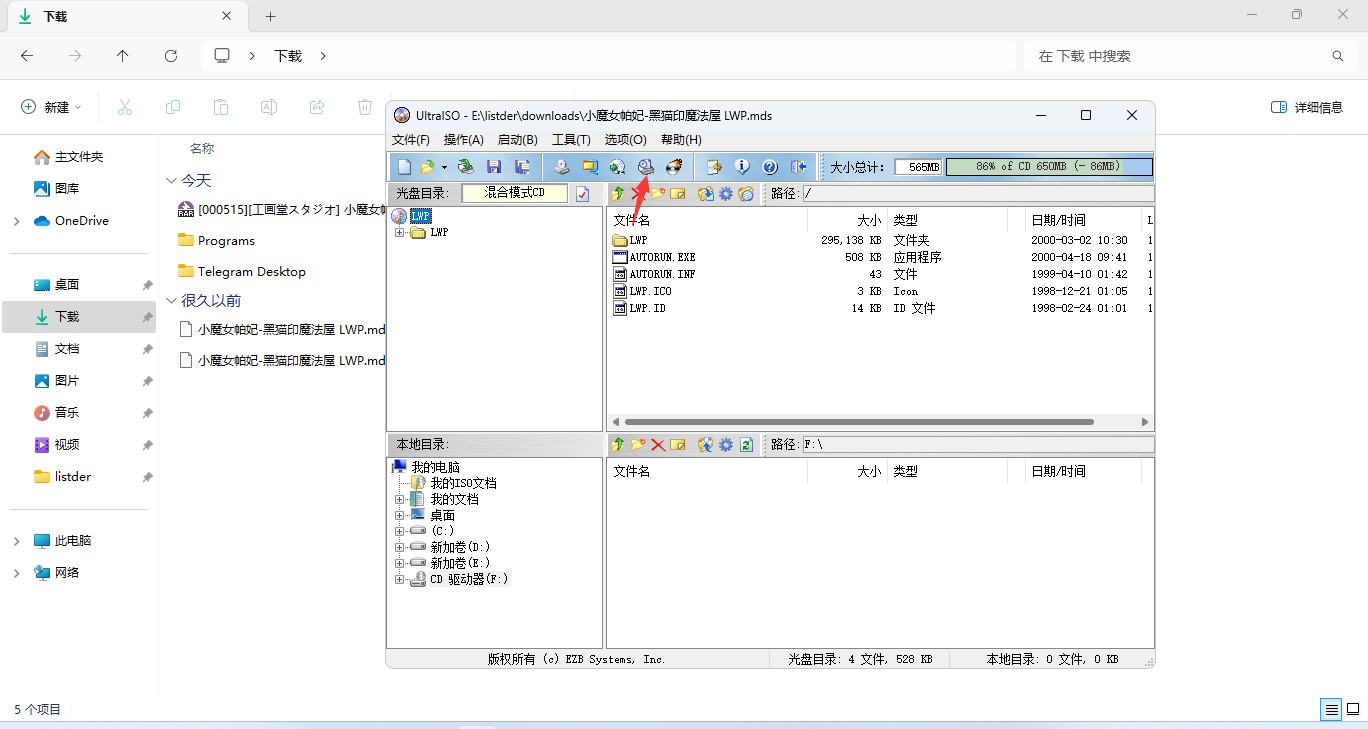
把这些东西全部解压出来观察我们解压后的文件结构
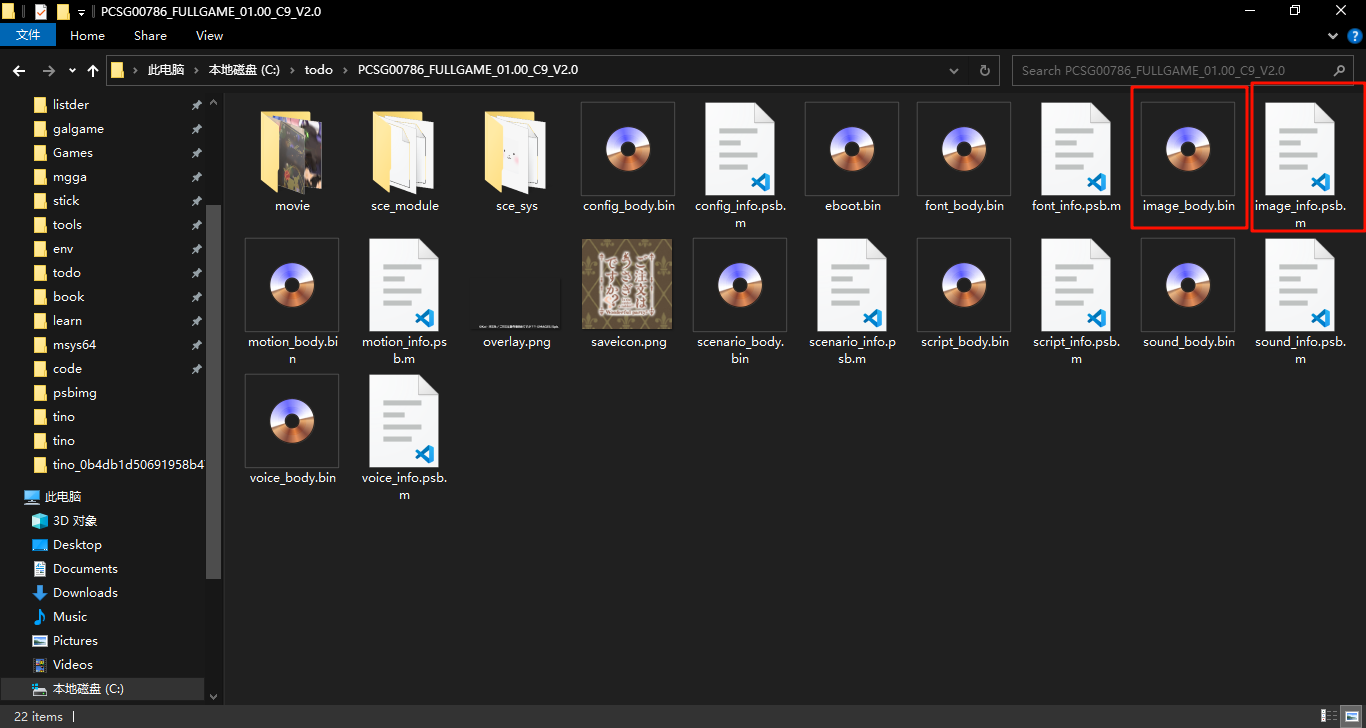
可以发现我们的主要要分析的文件应该是eboot.bin,xxx_info.psb.m和xxx_body.bin,这是因为movie文件夹内的文件已经是我们希望的.mp4这种常见格式,我们不需要去动他,而另外两个文件夹内的文件过小(因为Galgame存在图片和音频等各种媒体资源,所以一般情况下存放资源文件的档案不可能很小),我们应该避免先分析这些文件。
再根据文件大小 (image_body.bin 占 636MB 而 image_info.psb.m 仅仅只有 120KB )我们可以推断出 xxx_body.bin 为资源文件的主体部分,xxx_info.psb.m 应该为主体部分的配置文件或者索引之类的东西。
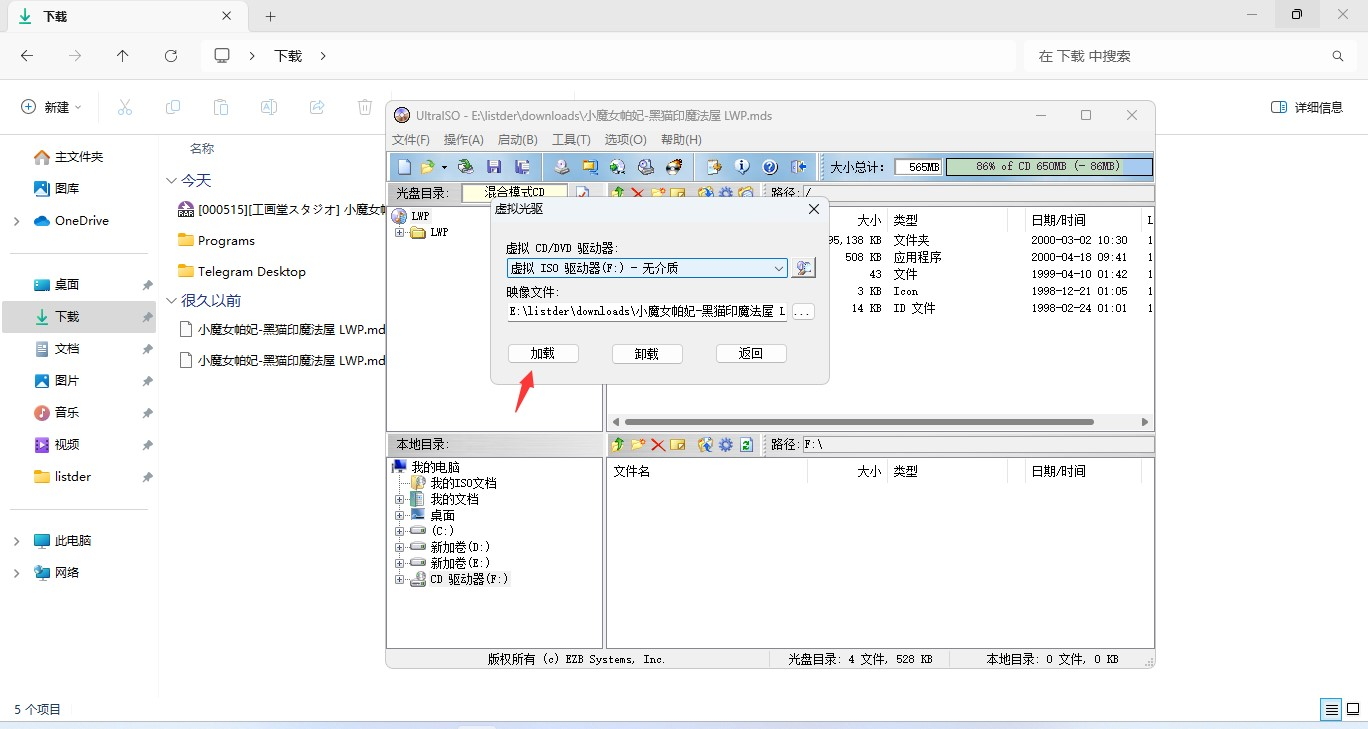
看到 .bin 这种东西,我们先用GARbro这种通用工具尝试(实际上GARbro无法解包),如果不行再尝试我们一开始说过的查找文件头的办法
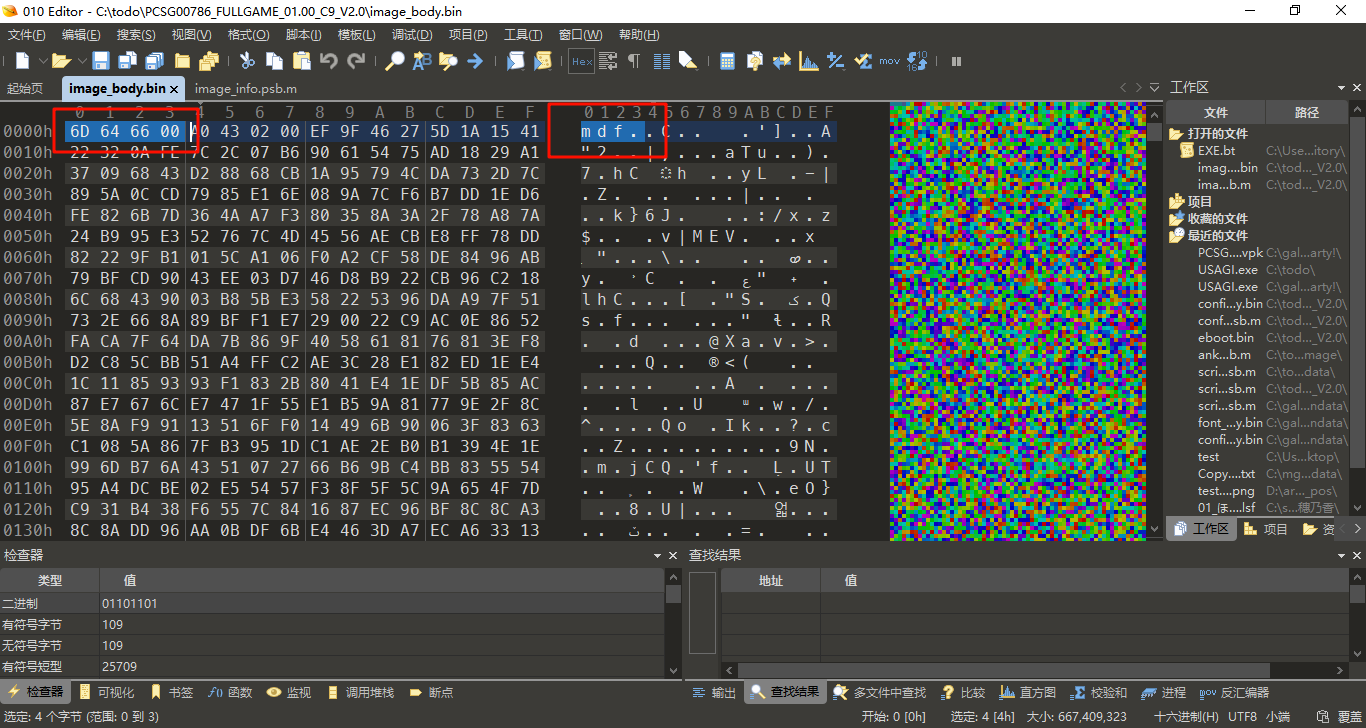
可以看到文件头为6D 64 66 00,查找可知
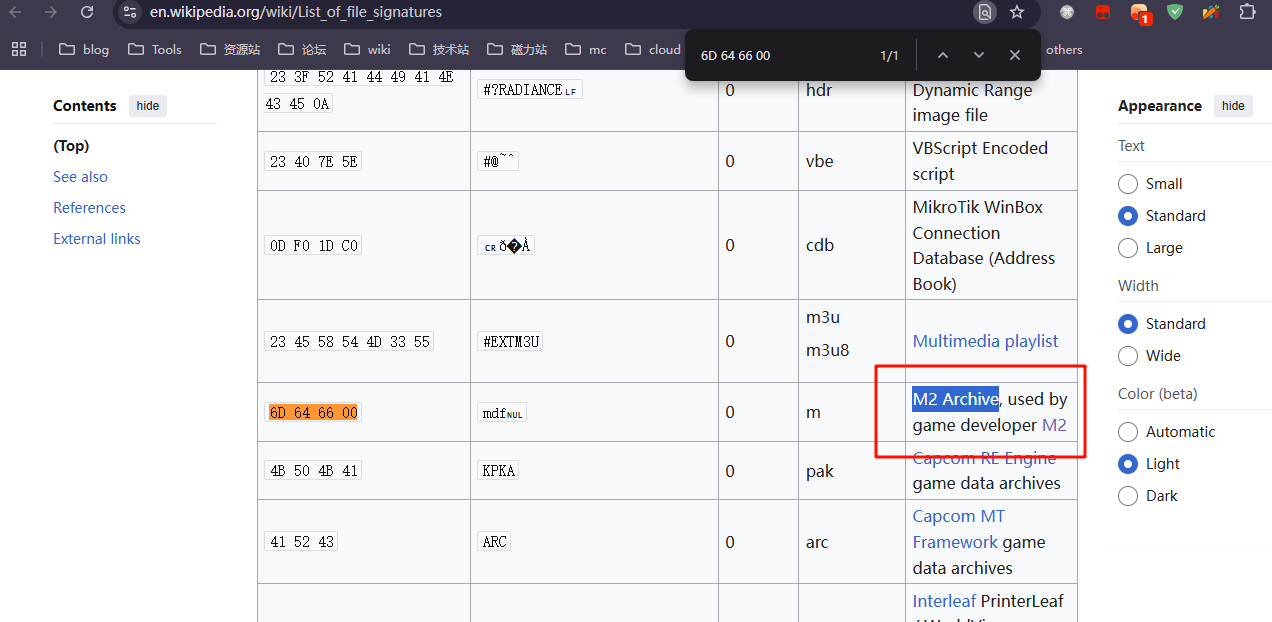
这是一个M2 Archive File,知道了这些必要信息后,我们可以Google搜索关键词来查找工具,注意,第一次搜索关键词越多越好,找不到再删除一些不确定的关键词来搜索
此处我们使用*_body.bin mdf m2 archive来搜索
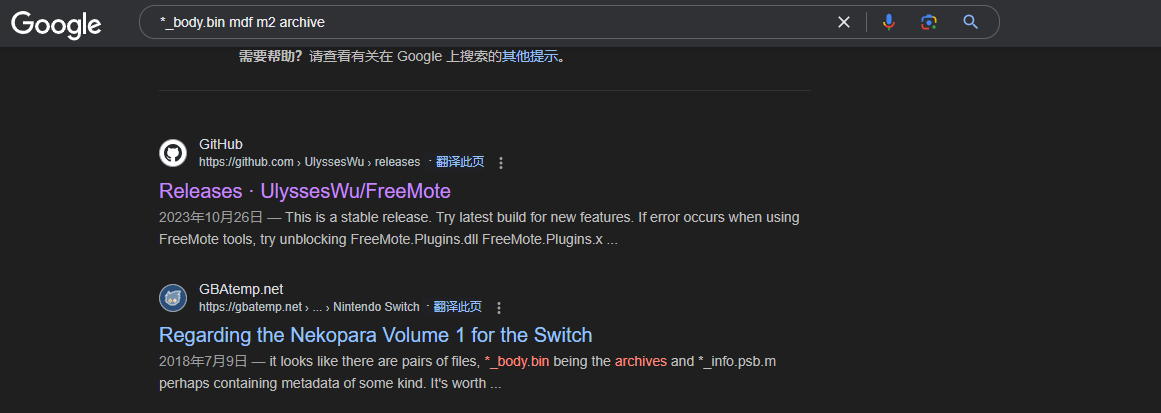
可以看到,第二个搜索结果中与我们的关键词十分匹配,点开查看可以知道
The engine the Switch version runs on is "Kaleido ADV Workshop" by M2.
There are tools to extract the *_body.bin and *_info.psb.m files, but you need an encryption key from the executable.
也就是说,这确实是一种叫做M2 Engine的引擎,解包他确实有特定的工具,但是我们需要知道这个密钥(贴子中没有指明具体的工具,所以我们重新查找m2 engine .bin 解包,这次因为我们已经知道了引擎名称,所以直接搜索)
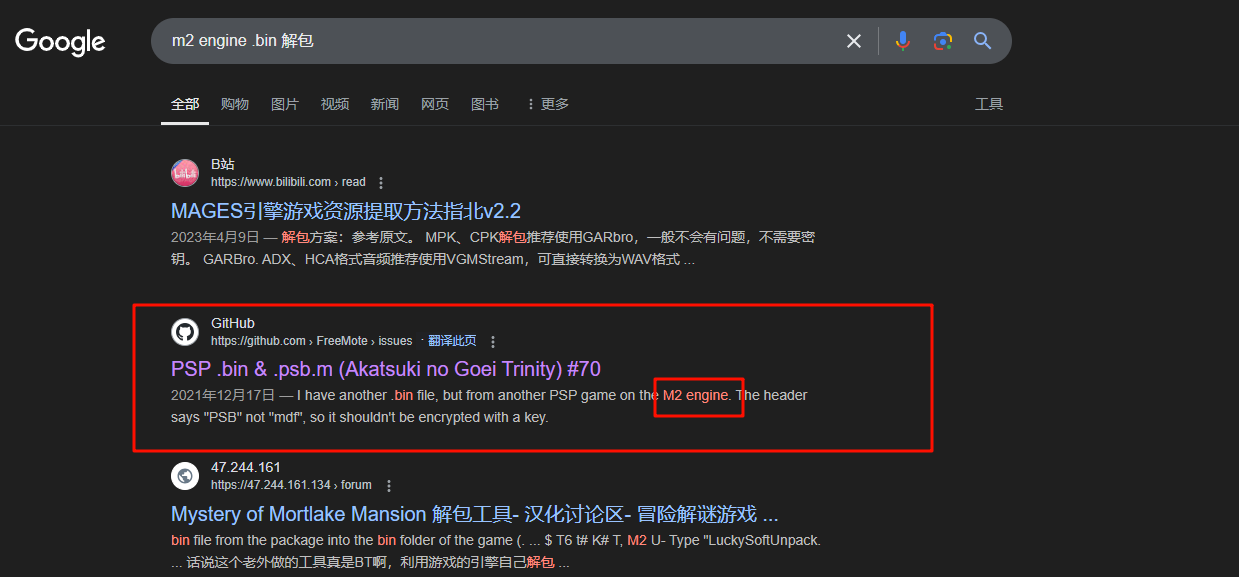
出现了一个GitHub链接,点开查看这个issue,发现这个issue主要是在讨论解包file_info.psb.m遇到的问题,顺带我们得知这个项目可以解包我们的M2 Archive File(这是一个叫做FreeMote的项目)。
既然找到工具了,那么这个时候我们应该返回项目主页查看具体的Readme.md也就是项目的介绍,通常此处会写明怎么使用这个项目(如果没有就翻翻Wiki之类的东西,再没有就去issue区慢慢研究怎么用...都没有的话,就只能请你自主阅读项目源码了),
FreeMote is a set of tool/libs for M2 Packaged Struct Binary file format. The file header usually starts with PSB/PSZ/mdf, and the file extensions usually are .psb|.psz|.mdf|.pimg|.scn|.mmo|.emtbytes|.mtn|.dpak|.psb.m.
显然,这个项目就是我们要找的工具,接着往下翻Readme可以看到
Read wiki for detailed usages.
接着查阅wiki可以得知
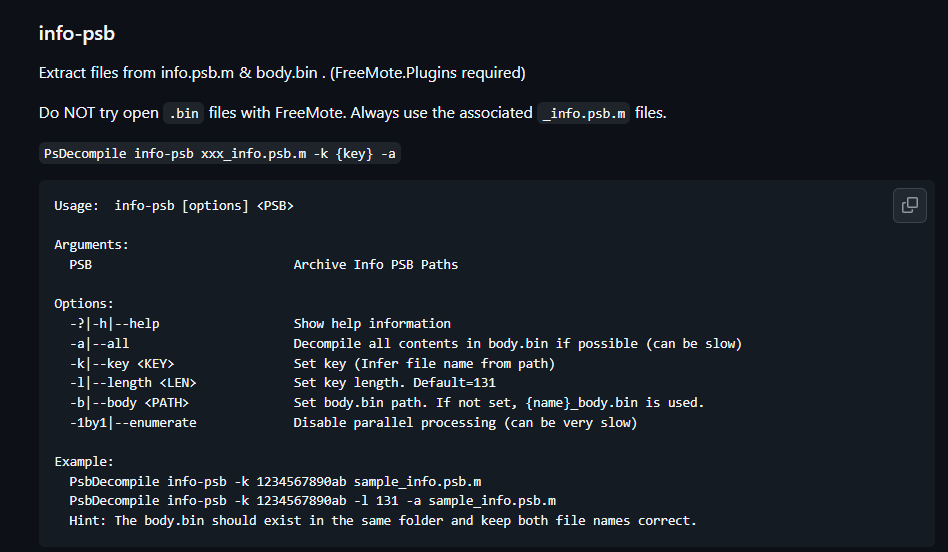
我们应该使用以下命令来解包我们的文件
PsDecompile info-psb xxx_info.psb.m -k {key} -a
那么我们的问题就变成了如何找到这个key
查阅wiki的PSB-Shells,-Types,-Platforms可以得知
Key: usually hex string (length = 13 for most cases, can be different for M2 games, such as 9, and there could be any string rather than just hex), e.g. 523aad2de7132, 38757621acf82, ae3bb93923bf8, Rj9Pegoh4
Seed: key + file name, e.g. 523aad2de7132font_info.psb.m, 38757621acf82voice_info.psb.m
但是我们并没有找到查找key的办法,这种情况我们应该查找issue,看看有没有人问过类似的问题
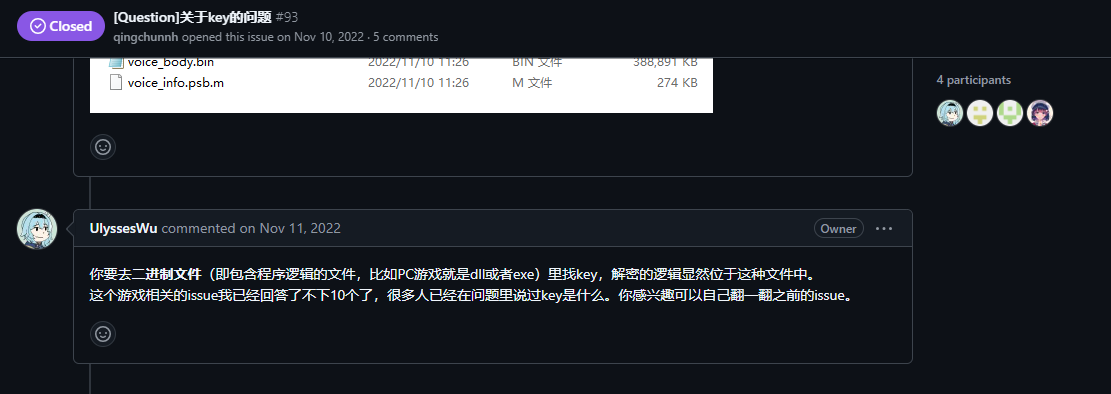
在issue #93下我们得知
你要去二进制文件(即包含程序逻辑的文件,比如PC游戏就是dll或者exe)里找key,解密的逻辑显然位于这种文件中。
也就是说,我们应该去eboot.bin下找(因为一番搜索得知eboot.bin是psv下的二进制文件)
虽然我们知道key的结构,可以暴力枚举出所有可能的key(即eboot.bin下所有长度为13的字符串)来进行尝试,但这也太麻烦了,所以我们继续查找相关issue
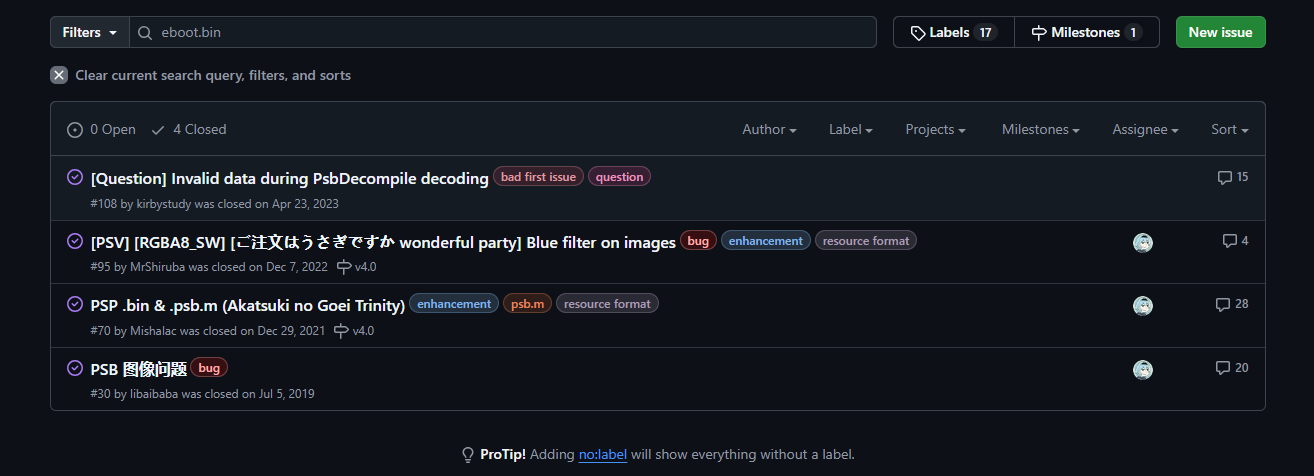
虽然在issue #95中我们已经得知了key的值为a23e898ef1032,但是我们想知道是找到key的方法
继续翻阅相关issue,在issue #30可以得知
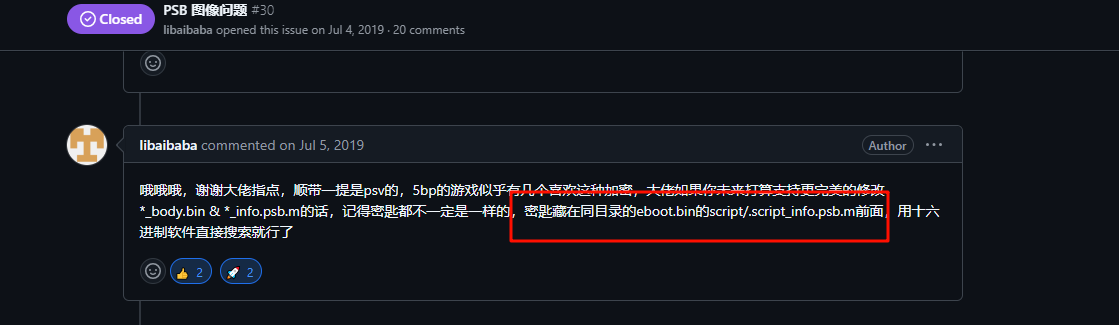
密匙藏在同目录的eboot.bin的script/.script_info.psb.m前面,用十六进制软件直接搜索就行了
我们直接尝试搜索
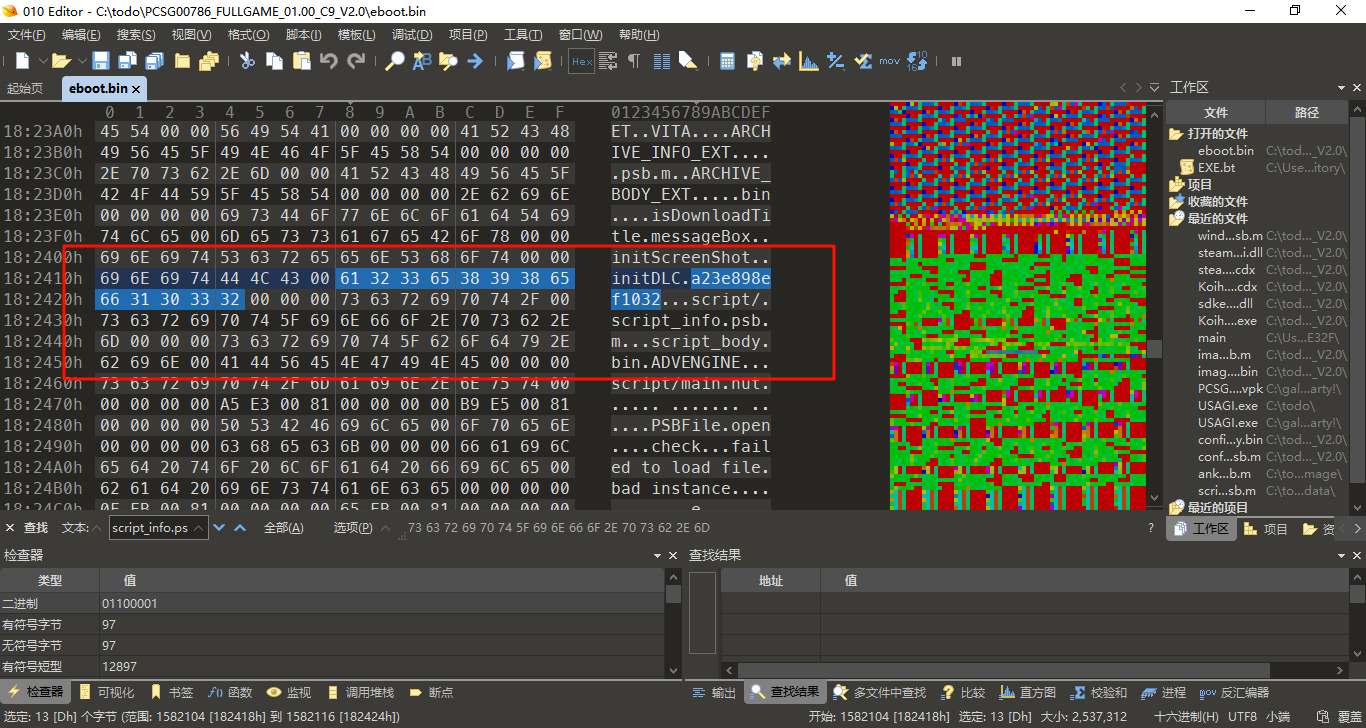
果然找到了密钥,证实了我们key的值确实为a23e898ef1032。
尝试运行
PsbDecompile.exe info-psb -k a23e898ef1032 sound_info.psb.m -a
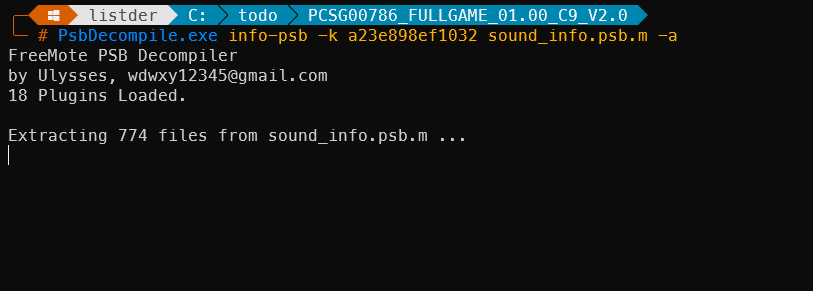
解包成功。
总结
多问,多思考
顺带附带一个立绘合成的DLC
DLC
合成立绘的关键是正确解读配置文件,找到正确的拼接方法(大多为查找(x,y)坐标然后直接覆盖即可)
此处以我们刚刚解包好的《ご注文はうさぎですか?? Wonderful Party!》(PSV)为例
显然,配置文件为.json,我们随便提取一个立绘组来进行研究
此处以tino_1cc1bc3c49e93177acc67700604fda8d为例
tino_1cc1bc3c49e93177acc67700604fda8d的配置文件有两个,一个为tino_1c876bf3986382099796dd6ea88266cc.psb.m.json另一个为tino_1c876bf3986382099796dd6ea88266cc.psb.m.resx.json
tino_1c876bf3986382099796dd6ea88266cc.psb.m.json:
{
"crop": {
"h": 574,
"w": 319,
"x": 1138,
"y": 170
},
"eyediff": {
"h": 55.0,
"w": 104.0,
"x": 1277.0,
"y": 321.0
},
"eyediffbase": 320,
"eyemap": {
"目目そらし": null,
"目目そらし1": 0,
"目目そらし2": 1
},
"h": 744,
"id": "image",
"imageList": [{
"height": 574,
"label": "tino_1c876bf3986382099796dd6ea88266cc",
"texture": [{
"height": 512.0,
"image": {
"height": 512,
"pixel": "#resource#1",
"type": "RGBA8_SW",
"width": 512
},
"left": 0.0,
"top": 0.0,
"width": 512.0
},{
"height": 64.0,
"image": {
"height": 64,
"pixel": "#resource#0",
"type": "RGBA8_SW",
"width": 512
},
"left": 0.0,
"top": 512.0,
"width": 512.0
}],
"width": 437
}],
"label": "",
"lipdiff": {
"h": 11.0,
"w": 8.0,
"x": 1332.0,
"y": 394.0
},
"lipdiffbase": 427,
"lipmap": {
"口目そらし": 0,
"口目そらし1": 1,
"口目そらし2": 2
},
"spec": "vita",
"version": 1.0,
"w": 2560
}
tino_1c876bf3986382099796dd6ea88266cc.psb.m.resx.json:
{
"PsbVersion": 3,
"PsbType": "Tachie",
"Platform": "vita",
"CryptKey": null,
"ExternalTextures": false,
"Context": {
"MdfKeyLength": 131,
"FileName": "tino_1c876bf3986382099796dd6ea88266cc.psb.m",
"MdfKey": "a23e898ef1032tino_1c876bf3986382099796dd6ea88266cc.psb.m",
"PsbZlibFastCompress": false,
"PsbShellType": "MDF"
},
"Resources": {
"0": "tino_1c876bf3986382099796dd6ea88266cc.psb.m/tino_1c876bf3986382099796dd6ea88266cc.png",
"1": "tino_1c876bf3986382099796dd6ea88266cc.psb.m/tino_1c876bf3986382099796dd6ea88266cc.png"
}
}
通过观察可以知道我们应该具体研究tino_1c876bf3986382099796dd6ea88266cc.psb.m.json。因为tino_1c876bf3986382099796dd6ea88266cc.psb.m.resx.json显然没有我们需要的数据。
接着我们看看图片

观察可知,所有的差分嵌在一张图片上,那么我们就需要把这些差分裁剪下来,然后再把基底裁剪出来进行覆盖
假如我们知道我们需要裁剪图片的左上角的坐标(x,y),以及他的长宽,我们就可以把这张图片裁剪出来
也就是说我们需要构造函数 cutimg(cv::Mat img, int x, int y, int w, int h) -> cv::Mat
然后通过读取配置文件我们可以很容易的获得这些参数,从而裁剪出所有差分和基底
接着我们只需要把差分覆盖在基底上,把文件输出即可,这个过程我们只需要知道这两张图片的相对坐标即可
也就是说我们还需要构造这么一个函数 coverimg(cv::Mat baseimg, cv::Mat faceimg, int x, int y) -> cv::Mat
这两个参数也可以通过读取配置文件然后进行一些简单的运算得出(通常为二者坐标之差取绝对值)
最后附上我的屎山()
#include <json/json.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <filesystem>
#include <json/value.h>
#include <vector>
#include <opencv4/opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <windows.h>
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
struct cimg{
int x, y, n;
std::string name;
};
void createcimg(std::string val, Json::Value &root, std::vector<cimg> &img);
void fixdcimg(std::vector<cimg> &img, int w, int h, int a, int basex);
Json::Value readjson(std::string file);
cv::Mat cutimg(cv::Mat img, int x, int y, int w, int h);
cv::Mat coverimg(cv::Mat baseimg, cv::Mat faceimg, int x, int y);
void work(std::string pngfile, std::string inputfile, std::string basename);
int main(int argc,char* argv[]){
fs::create_directory("output");
for (const auto& entry : fs::directory_iterator(".")) {
if (fs::is_regular_file(entry.status())) {
fs::path file_path = entry.path();
std::string filename = file_path.filename().string();
if (filename.find(".psb.m.json") != std::string::npos) {
std::string inputfile = filename;
std::string basename = filename.substr(0,filename.size() - 11);
std::string pngfile = "./" + basename + ".psb.m/" + basename + ".png";
work(pngfile, inputfile, basename);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
Json::Value readjson(std::string file){
std::ifstream jsonfile(file, std::ifstream::binary);
Json::Value root;
Json::CharReaderBuilder readerBuilder;
std::string errs;
Json::parseFromStream(readerBuilder, jsonfile, &root, &errs);
return root;
}
void createcimg(std::string val,Json::Value &root,std::vector<cimg> &img){
Json::Value::Members members;
members = root[val.c_str()].getMemberNames();
int num = 0;
for (Json::Value::Members::iterator iterMember = members.begin(); iterMember != members.end(); iterMember++){
cimg temp;
std::string strKey = *iterMember;
if (root[val.c_str()][strKey.c_str()].isNull()) {
temp.name = strKey.c_str();
temp.n = -1;
num--;
}
else{
temp.name = strKey.c_str();
temp.n = num;
}
img.push_back(temp);
num ++;
}
return ;
}
void fixdcimg(std::vector<cimg> &img, int w, int h, int a, int basex){
for (int i = 0; i < img.size(); i++){
if(img[i].n == -1){
img[i].x = -1;
img[i].y = -1;
}
else{
img[i].x = basex + (img[i].n / a) * w;
img[i].y = (img[i].n % a) * h;
}
}
}
cv::Mat cutimg(cv::Mat img, int x, int y, int w, int h){
cv::Rect cropRegion(x, y, w, h);
cropRegion = cropRegion & cv::Rect(0, 0, img.cols, img.rows);
return img(cropRegion).clone();
}
cv::Mat coverimg(cv::Mat baseimg, cv::Mat faceimg, int x, int y){
cv::Mat output = baseimg.clone();
for (int i = 0; i < faceimg.rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < faceimg.cols; ++j) {
int targetX = x + j;
int targetY = y + i;
if (targetX >= 0 && targetX < baseimg.cols && targetY >= 0 && targetY < baseimg.rows) {
cv::Vec4b facePixel = faceimg.at<cv::Vec4b>(i, j);
if (facePixel[3] > 0) {
output.at<cv::Vec4b>(targetY, targetX) = facePixel;
}
}
}
}
return output;
}
void work(std::string pngfile, std::string inputfile, std::string basename){
Json::Value root = readjson(inputfile);
int eyex = abs(root["crop"]["x"].asInt() - root["eyediff"]["x"].asInt()) -1;
int eyey = abs(root["crop"]["y"].asInt() - root["eyediff"]["y"].asInt()) -1;
int h = root["crop"]["h"].asInt(),
w = root["crop"]["w"].asInt(),
eyeh = root["eyediff"]["h"].asInt() + 2,
eyew = root["eyediff"]["w"].asInt() + 2,
eyediffbase = root["eyediffbase"].asInt(),
eyediffend = root["h"].asInt();
std::vector<cimg> eyemap;
createcimg("eyemap",root,eyemap);
fixdcimg(eyemap,eyew,eyeh,h/eyeh,eyediffbase);
int lipx, lipy, liph, lipw, lipdiffbase;
std::vector<cimg> lipmap;
createcimg("lipmap",root,lipmap);
if(root["lipdiffbase"].isNull()) {
lipx = -1,
lipy = -1,
liph = -1,
lipw = -1,
lipdiffbase = -1;
}
else{
lipx = abs(root["crop"]["x"].asInt() - root["lipdiff"]["x"].asInt()),
lipy = abs(root["crop"]["y"].asInt() - root["lipdiff"]["y"].asInt()),
liph = root["lipdiff"]["h"].asInt() + 2,
lipw = root["lipdiff"]["w"].asInt() + 2,
lipdiffbase = root["lipdiffbase"].asInt();
fixdcimg(lipmap, lipw, liph, h/liph, lipdiffbase);
}
cv::Mat img = cv::imread(pngfile, cv::IMREAD_UNCHANGED);
int num = eyemap.size();
cv::Mat baseimg = cutimg(img, 0, 0, w, h);
for(int i = 0; i < num; i++){
cv::Mat out;
if(eyemap[i].n != -1 && lipmap[i].n != -1){
cv::Mat eyecut = cutimg(img, eyemap[i].x, eyemap[i].y, eyew, eyeh);
cv::Mat lipcut = cutimg(img, lipmap[i].x, lipmap[i].y, lipw, liph);
out = coverimg(baseimg, eyecut, eyex, eyey);
out = coverimg(out, lipcut, lipx, lipy);
}
else if(eyemap[i].n != -1 && lipmap[i].n == -1){
cv::Mat eyecut = cutimg(img, eyemap[i].x, eyemap[i].y, eyew, eyeh);
out = coverimg(baseimg, eyecut, eyex, eyey);
}
else{
out = baseimg;
}
fs::path filename = "./output/"+ basename + "_" + eyemap[i].name + "_" + lipmap[i].name + ".png";
cv::imwrite(filename.string(), out);
}
}